|
|
| ||
Urban Land Use
Not only do cities have a central business district, but they also have subcenters and suburban areas as well as many other different types of land use taking place. Each city is unique in the type of subcenters it has although some parallel each other pretty closely. Most people tend to live in the suburban areas and if they have a job closer to the central city then they will commute to their jobs. Wages are generally higher within the city because the commute from the suburbs is longer so people feel they should be compensated for that. If they were to work closer to their residence they would be willing to give up more income because it would be less of a commute and there are many costs associating with commuting. To learn more about commuting costs go to our section on Automobile Externalities.
The distance to the city's edge is set by the population and the rent here and the agricultural rent will never change. At this point the quantity of land supplied will equal the quantity of land demanded. To illustrate this concept consider this graph:
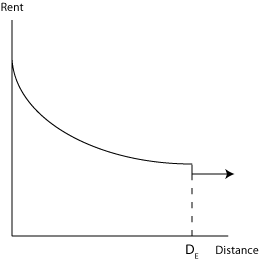
As you move closer in to the city the population density will increase. People will be willing to give up more land at lower rents in order to live in the city possibly closer to where they work. They will pay in the form of higher rents in order to not have to commute, but the wages will compensate for the higher rents.
Urban Sprawl
This is the case when people choose to keep moving farther from the city as the population increases instead of building up within the city. This makes the city larger in area and it will keep growing and growing as long as there is more land to occupy. If there is a lower density within a major city this means that there is a high level of sprawl. The density of cities is vastly different among nations. In the United States cities are not nearly as dense as many of the major European cities. To learn more about the differences visit our section on Comparing United States and European Cities.
Causes of Sprawl:
- Urban Disamenities: These would be things that are congestion externalities such as high crime, more noise due to traffic, dirtier, denser, and less privacy.
- Mortgage Subsidy: Providing subsidies increases housing consumption and also increases lot sizes thus decreasing density.
- Filtering: There is underpricing of fringe infrastructure because the cost of new development is not borne fully by the developers or their consumers. So the sub-divisions on the outskirts of the cities become more affordable to city residents.
- Zoning: Some places establish minimum lot sizes so they have no choice but to build out.
- Income Increases: If one's income increases, this will also increase their demand for lot size.
- Low value of Agricultural Land: There are lower rents here so lot sizes are larger.
- Tiebout Sorting: People will sort based on their preferences for amenities and public services.
To understand more about land-use visit our section on Land Use in Anchorage, Alaska.
| Copyright 2006 Experimental Economics Center. All rights reserved. | Send us feedback |