|
|
|
The following section is intended for intermediate/upper intermediate students who are familiar with optimization techniques. It summarizes the differences between the market and Pareto efficient outcomes in mathematical form.
|
|
The individual i chooses how much of the public good to buy on his own ( i) to maximize his utility ui(x, yi) from consuming the public good x and private consumption yi, taking contributions of others as given (x-i). The consumer's problem can be then written as follows
: i) to maximize his utility ui(x, yi) from consuming the public good x and private consumption yi, taking contributions of others as given (x-i). The consumer's problem can be then written as follows
:
|
|
max ui(x, yi) = ui(x-i +  i, yi) subject to constraints i, yi) subject to constraints  i, yi i, yi  0 and to p. 0 and to p. i + yi i + yi  m, m,
where p denotes the price of one unit of the public good and m denotes the value of i-th person initial endowment or income.
|
|
First order conditions:
MRSi  p, and MRSi = p if p, and MRSi = p if  > 0. > 0.
|

|
|
Suppose a unit of public good costs 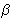 and the consumer i has a utility function of the following form: and the consumer i has a utility function of the following form:
ui(x, yi) = yi +  ilog x for all i = 1,...,n. ilog x for all i = 1,...,n.
Then MRSi =  i / x i / x
Let A =  i i i and i and  * = max { * = max { i | i i | i  N }. N }.
|
|
Pareto Efficiency:
 MRSi = p MRSi = p
i.e.,  ( ( i / x) = i / x) = 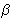
(1 / x) A = 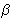
x´ = A / 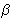 , where x´ is the Pareto efficient outcome. , where x´ is the Pareto efficient outcome.
|
|
Market Outcome:
MRSi  p = p = 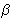 , for all i , for all i
i.e.,  i / x i / x  p, for all i p, for all i
i.e., x   i / p, for all i. i / p, for all i.
Let's examine when an idividual purchases positive amount of public good
MRSi = p if  i > 0, i.e., x = i > 0, i.e., x =  i / i / 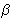 . .
From this follows that  i = 0 if i = 0 if  i < i <  * = max { * = max { i | i i | i  N }, and xm = N }, and xm =  * / * / 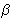 , where xm denotes the market outcome. , where xm denotes the market outcome.
Note that  * << A and therefore, xm << x´, meaning that the market outcome is severly inefficient. * << A and therefore, xm << x´, meaning that the market outcome is severly inefficient.
|
| |